Revolutionizing Manufacturing Processes: The Power of MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems)
In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, staying competitive requires more than just advanced machinery and skilled labor. Manufacturers must embrace digital transformation and leverage technology to optimize their production processes. Among the many groundbreaking innovations, one system that has emerged as a game-changer is the Manufacturing Execution System (MES). This article explores the fundamental concepts of MES and highlights its immense potential to revolutionize manufacturing processes across industries.

Understanding MES:
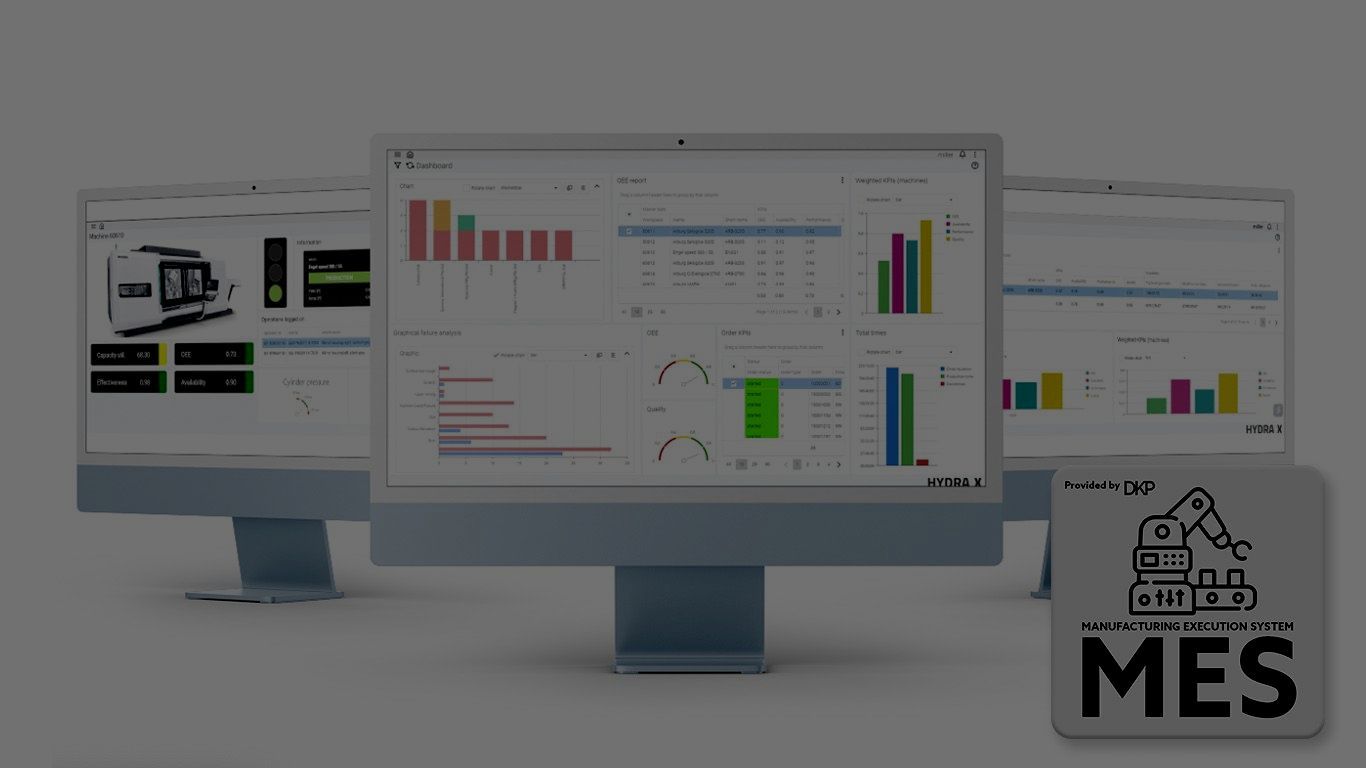
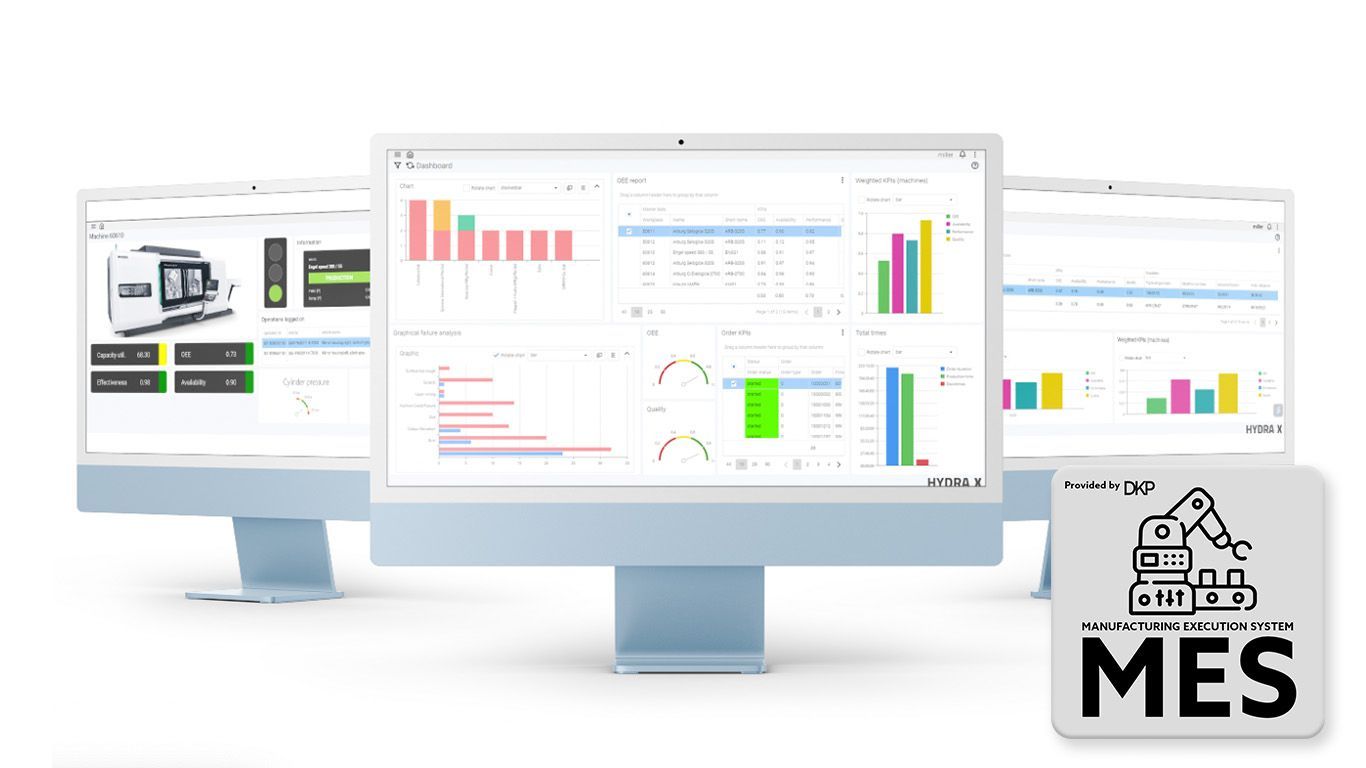
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a comprehensive software solution that bridges the gap between enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and the shop floor. MES serves as the central nervous system of manufacturing operations, orchestrating, and optimizing the entire production process in real-time. It provides a wealth of functionalities, including production scheduling, material tracking, quality control, equipment management, and performance analysis.
Key Features and Benefits:
1. Real-Time Production Visibility: MES provides real-time visibility into production processes, enabling manufacturers to monitor operations, track progress, and identify bottlenecks promptly. This facilitates proactive decision-making, ensuring maximum efficiency and productivity.
2. Streamlined Workflows: By automating and standardizing manufacturing workflows, MES eliminates manual processes and reduces the risk of errors. It facilitates seamless communication between different departments, suppliers, and stakeholders, resulting in improved coordination and reduced lead times.
3. Quality Assurance and Compliance: MES integrates quality control processes into production, enabling manufacturers to enforce stringent quality standards. It provides real-time data on product quality, allowing for timely interventions to prevent defects and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
4. Inventory and Material Management: With MES, manufacturers can track and manage their inventory levels, ensuring optimal stock levels and minimizing waste. Real-time material tracking and automated replenishment systems streamline supply chain management, reducing stockouts and inventory carrying costs.
5. Performance Analysis and Continuous Improvement: MES generates comprehensive reports and analytics on production performance, allowing manufacturers to identify areas for improvement. Data-driven insights enable informed decision-making, driving operational excellence, and continuous improvement initiatives.

Implementing MES:
Successful implementation of MES requires careful planning and collaboration between IT, operations, and management teams. It is crucial to define clear objectives, assess organizational readiness, select a suitable MES solution, and develop an implementation roadmap. Additionally, training and change management programs play a vital role in ensuring smooth adoption and maximizing the benefits of MES.
Challenges and Considerations:
While MES offers significant advantages, it is essential to address potential challenges. Integration with existing systems, such as ERP and shop floor equipment, requires careful planning and may involve complex interfaces. Data security and protection are critical considerations when implementing MES, as it involves the collection and analysis of sensitive production data. Manufacturers must also consider scalability and flexibility to accommodate evolving business needs and industry trends.
Future Outlook:
As Industry 4.0 gains momentum, the role of MES becomes even more crucial. With the integration of emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and predictive analytics, MES has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing processes further. Smart factories equipped with MES will drive automation, optimization, and data-driven decision-making, paving the way for increased productivity, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Conclusion:
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) have emerged as a transformative force in the manufacturing industry, empowering organizations to optimize production processes, improve quality, and boost operational efficiency. By providing real-time visibility, streamlining workflows, and enabling data-driven decision-making, MES is revolutionizing the way manufacturers operate. As manufacturers embrace digital transformation and Industry 4.0, integrating MES into their operations will become increasingly vital for sustained success in the competitive global marketplace.